What Values Cannot Be Probabilities
What are Events in Probability?
A probability event can be divers as a set up of outcomes of an experiment. In other words, an event in probability is the subset of the respective sample space. And so, what is sample space?
The entire possible gear up of outcomes of a random experiment is the sample space or the individual space of that experiment. The likelihood of occurrence of an event is known as probability. The probability of occurrence of any effect lies betwixt 0 and ane.
Events In Probability
The sample space for the tossing of iii coins simultaneously is given by:
S = {(T , T , T) , (T , T , H) , (T , H , T) , (T , H , H ) , (H , T , T ) , (H , T , H) , (H , H, T) ,(H , H , H)}
Suppose, if nosotros want to find only the outcomes which accept at least ii heads; and then the set of all such possibilities can be given as:
E = { (H , T , H) , (H , H ,T) , (H , H ,H) , (T , H , H)}
Thus, an outcome is a subset of the sample space, i.e., East is a subset of S.
There could be a lot of events associated with a given sample space. For any issue to occur, the upshot of the experiment must be an chemical element of the gear up of event Eastward.
What is the Probability of Occurrence of an Event?
The number of favourable outcomes to the full number of outcomes is defined as the probability of occurrence of any event. So, the probability that an event will occur is given equally:
P(E) = Number of Favourable Outcomes/ Full Number of Outcomes
Types of Events in Probability:
Some of the important probability events are:
- Impossible and Certain Events
- Simple Events
- Chemical compound Events
- Contained and Dependent Events
- Mutually Exclusive Events
- Exhaustive Events
- Complementary Events
- Events Associated with "OR"
- Events Associated with "AND"
- Event E1 but not E2
Impossible and Sure Events
If the probability of occurrence of an result is 0, such an event is called an impossible result and if the probability of occurrence of an upshot is 1, it is called a sure consequence. In other words, the empty fix ϕ is an incommunicable event and the sample infinite S is a sure event.
Simple Events
Whatever event consisting of a single point of the sample space is known as a uncomplicated event in probability. For example, if S = {56 , 78 , 96 , 54 , 89} and E = {78} then E is a unproblematic event.
Compound Events
Contrary to the elementary issue, if whatsoever outcome consists of more than 1 single point of the sample space then such an event is called a chemical compound event. Considering the same example again, if South = {56 ,78 ,96 ,54 ,89}, E1 = {56 ,54 }, Eastward2 = {78 ,56 ,89 } then, Eone and Etwo stand for two compound events.
Independent Events and Dependent Events
If the occurrence of any issue is completely unaffected by the occurrence of any other event, such events are known as an independent consequence in probability and the events which are affected by other events are known as dependent events.
Mutually Exclusive Events
If the occurrence of one event excludes the occurrence of some other event, such events are mutually exclusive events i.eastward. ii events don't have any common point. For example, if Southward = {1 , two , 3 , 4 , 5 , half dozen} and Ei, Etwo are two events such that E1 consists of numbers less than iii and E2 consists of numbers greater than 4.
Then, E1 = {one,2} and E2 = {v,6} .
Then, E1 and E2 are mutually sectional.
Exhaustive Events
A gear up of events is called exhaustive if all the events together consume the entire sample space.
Complementary Events
For any event Eane at that place exists another upshot E1' which represents the remaining elements of the sample space S.
E1 = S − Due eastone'
If a dice is rolled then the sample space Due south is given as Due south = {ane , 2 , iii , 4 , five , six }. If outcome E1 represents all the outcomes which is greater than four, then Eastwardone = {5, half dozen} and Ei' = {1, 2, 3, 4}.
Thus Eastone' is the complement of the issue East1.
Similarly, the complement of Eane, East2, East3……….Eastn will be represented as E1', Due east2', Due east3'……….En'
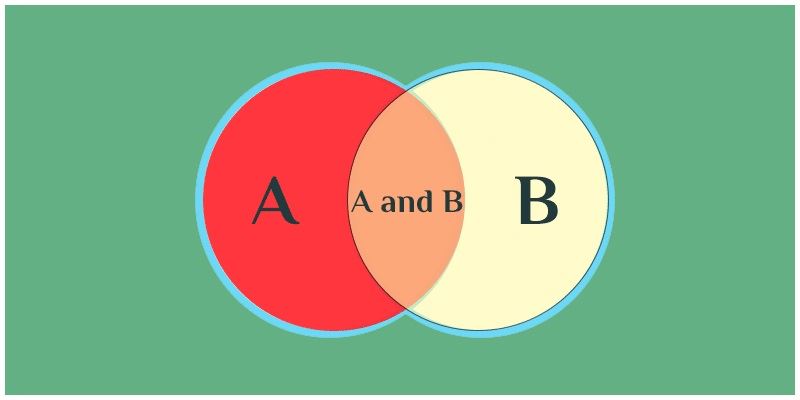
Events Associated with "OR"
If two events Eone and E2 are associated with OR and so it means that either E1 or E2 or both. The marriage symbol (∪) is used to represent OR in probability.
Thus, the event E1U Eii denotes E1 OR E2.
If we have mutually exhaustive events Eane, E2, Ethree ………En associated with sample space S and so,
E1 U E2 U E3U ………En = S
Events Associated with "AND"
If two events E1 and Eastward2 are associated with AND and so information technology means the intersection of elements which is common to both the events. The intersection symbol (∩) is used to represent AND in probability.
Thus, the result Ei ∩ E2 denotes E1 and E2.
Effect Ei only non E2
It represents the deviation between both the events. Event Eastwardane only not E2 represents all the outcomes which are present in Eane only not in Etwo. Thus, the event Due east1 simply non Easttwo is represented as
E1, Eastwardii = Ei – Eii
Types of Events In Probability
Example Question on Probability of Events
Question: In the game of snakes and ladders, a off-white dice is thrown. If result Ei represents all the events of getting a natural number less than 4, upshot East2 consists of all the events of getting an even number and Eastwardiii denotes all the events of getting an odd number. List the sets representing the following:
i)E1 or E2 or Eastiii
ii)Due eastane and East2 and E3
iii)E1 but not E3
Solution:
The sample infinite is given as S = {i , 2 , 3 , 4 , v , 6}
E1 = {1,two,iii}
Eastward2 = {two,four,6}
E3 = {1,3,5}
i)Eone or Eii or Ethree= East1 E2 Eastward3= {i, 2, 3, 4, 5, vi}
ii)Eane and Due east2 and E3 = Due easti Eastward2 Eiii = ∅
3)E1 but not E3 = {2}
Probability Related Video:

More Topics Related to Probability Events
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Events in Probability?
In probability, events are the outcomes of an experiment. The probability of an event is the measure of the run a risk that the upshot volition occur as a result of an experiment.
What is the Difference Between Sample Space and Consequence?
A sample infinite is a collection or a set up of possible outcomes of a random experiment while an event is the subset of sample space. For example, if a die is rolled, the sample space will be {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} and the result of getting an even number volition be {ii, 4, half-dozen}.
What is the Probability of an Incommunicable Event and a Sure Event?
The probability of a certain upshot is always 1 while the probability of an impossible event is always 0.
What is an Example of an Incommunicable Upshot?
An instance of an impossible event will exist getting a number greater than 6 when a die is rolled.
What is meant by complementary events?
In probability, 2 events are said to be complementary if i event takes place if and simply if the other issue does not take place.
What are the dissimilar types of events in probability?
The unlike types of events in probability are complementary events, unproblematic events, chemical compound events, certain events, impossible events, dependent events, independent events, mutually exclusive events, exhaustive events, etc.
Are complementary events mutually exclusive?
Yeah, complementary events are mutually exclusive. This represents that the events that are complementary never happen at the same time.
What is meant by an independent event?
In probability, the independent events are the events that exercise not depend on the occurrence of the other outcome. In other words, an event which is not afflicted by the other event is chosen an independent event.
What Values Cannot Be Probabilities,
Source: https://byjus.com/maths/types-of-events-in-probability/
Posted by: patelstemed1965.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Values Cannot Be Probabilities"
Post a Comment